Background
This blog explores the transformative potential of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in optimizing supply chain operations. It delves into various applications of these technologies, highlighting how they can improve efficiency, reduce costs, enhance resilience, and drive better decision-making across the entire supply chain ecosystem.
Introduction
Supply chains are complex, dynamic systems involving numerous stakeholders, processes, and data points. Traditional methods often struggle to effectively manage this complexity, leading to inefficiencies, delays, and increased costs. AI and ML offer powerful tools to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, predict future trends, and automate tasks, thereby revolutionizing supply chain management.
Key Applications of AI/ML in Supply Chain
Here are some key areas where AI and ML are making a significant impact:
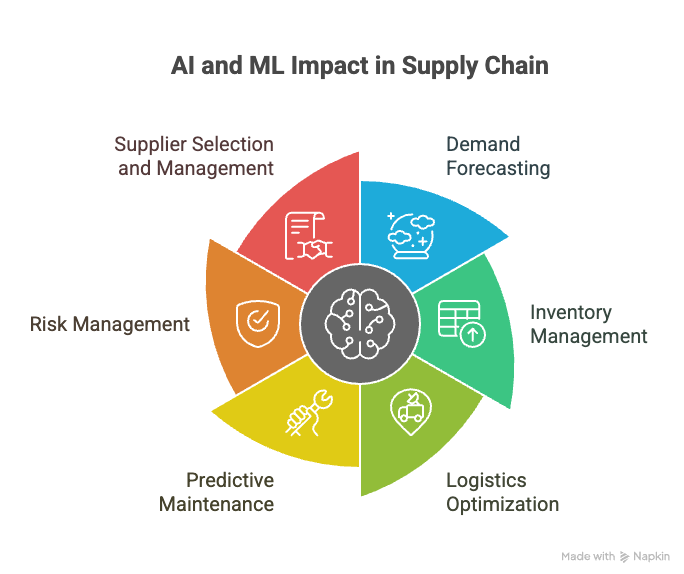
1. Demand Forecasting
- Challenge: Accurate demand forecasting is crucial for optimizing inventory levels, production planning, and resource allocation. Traditional forecasting methods often rely on historical data and statistical models, which may not be effective in capturing the impact of external factors such as market trends, seasonality, and promotions.
- AI/ML Solution: ML algorithms can analyze a wide range of data sources, including historical sales data, market trends, social media sentiment, and economic indicators, to generate more accurate and granular demand forecasts. This enables businesses to optimize inventory levels, reduce stockouts, and minimize waste.
- Example: Using time series forecasting models like ARIMA or more advanced deep learning models like LSTMs to predict future demand based on historical sales data and external factors.
2. Inventory Management
- Challenge: Maintaining optimal inventory levels is a delicate balancing act. Too much inventory ties up capital and increases storage costs, while too little inventory can lead to stockouts and lost sales.
- AI/ML Solution: AI/ML can optimize inventory levels by predicting demand fluctuations, identifying slow-moving items, and recommending optimal reorder points. This helps businesses reduce inventory holding costs, minimize stockouts, and improve customer satisfaction.
- Example: Implementing a dynamic inventory management system that uses reinforcement learning to learn the optimal inventory levels for each product based on real-time demand and supply conditions.
3. Logistics Optimization
- Challenge: Optimizing logistics operations, including transportation routing, warehouse management, and delivery scheduling, is essential for reducing costs and improving efficiency.
- AI/ML Solution: AI/ML can optimize logistics operations by identifying the most efficient routes, predicting delivery times, and automating warehouse processes. This helps businesses reduce transportation costs, improve delivery speed, and enhance customer satisfaction.
- Example: Using route optimization algorithms to determine the most efficient delivery routes based on real-time traffic conditions, delivery schedules, and vehicle capacity.
4. Predictive Maintenance
- Challenge: Equipment failures can disrupt supply chain operations, leading to delays and increased costs.
- AI/ML Solution: AI/ML can predict equipment failures by analyzing sensor data and identifying patterns that indicate potential problems. This enables businesses to perform proactive maintenance, reducing downtime and improving equipment reliability.
- Example: Implementing a predictive maintenance system that uses machine learning to analyze sensor data from manufacturing equipment and predict when maintenance is required.
5. Risk Management
- Challenge: Supply chains are vulnerable to a variety of risks, including natural disasters, political instability, and supplier disruptions.
- AI/ML Solution: AI/ML can identify and assess supply chain risks by analyzing data from various sources, including news feeds, weather reports, and supplier performance data. This enables businesses to develop mitigation strategies and improve supply chain resilience.
- Example: Using natural language processing (NLP) to analyze news articles and social media feeds to identify potential supply chain disruptions, such as labor strikes or political unrest.
6. Supplier Selection and Management
- Challenge: Choosing the right suppliers and managing their performance is critical for ensuring supply chain efficiency and reliability.
- AI/ML Solution: AI/ML can analyze supplier data, including financial performance, quality metrics, and delivery times, to identify the best suppliers and monitor their performance. This helps businesses reduce supplier risk and improve supply chain performance.
- Example: Developing a supplier scoring system that uses machine learning to evaluate suppliers based on a variety of factors, such as price, quality, and delivery performance.
Benefits of AI/ML in Supply Chain
The adoption of AI and ML in supply chain operations offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Efficiency: Automation of tasks and optimization of processes lead to significant efficiency gains.
- Reduced Costs: Optimized inventory levels, transportation routes, and maintenance schedules result in lower costs.
- Enhanced Resilience: Proactive risk management and mitigation strategies improve supply chain resilience.
- Better Decision-Making: Data-driven insights enable better decision-making across the entire supply chain.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: Improved delivery speed, reduced stockouts, and enhanced customer service lead to higher customer satisfaction.
Challenges and Considerations
While the potential benefits of AI/ML in supply chain are significant, there are also challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
- Data Quality: AI/ML algorithms require high-quality data to function effectively.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating AI/ML solutions with existing systems can be complex and time-consuming.
- Skills Gap: Implementing and managing AI/ML solutions requires specialized skills.
- Ethical Considerations: It’s important to consider the ethical implications of using AI/ML in supply chain, such as bias in algorithms and job displacement.
- Security: Protecting sensitive supply chain data from cyber threats is crucial.
Conclusion
AI and ML are transforming supply chain operations, enabling businesses to improve efficiency, reduce costs, enhance resilience, and drive better decision-making. By embracing these technologies, organizations can unlock significant value and gain a competitive advantage in today’s dynamic and complex global marketplace. However, careful planning, data management, and consideration of ethical implications are essential for successful implementation.