Background
This blog explores the complexities of measuring the Return on Investment (ROI) of Artificial Intelligence (AI) initiatives. It delves into the challenges associated with quantifying AI’s impact, outlines key metrics for evaluation, and provides a framework for effectively tracking and demonstrating the value generated by AI investments. By understanding these principles, organizations can make informed decisions about AI adoption, optimize their AI strategies, and ensure that AI initiatives deliver tangible business benefits.
The Challenge of Measuring AI ROI
Measuring the ROI of AI projects presents unique challenges compared to traditional IT investments. These challenges stem from several factors:
- Intangible Benefits: AI often delivers intangible benefits such as improved customer experience, enhanced decision-making, and increased employee productivity, which are difficult to quantify in monetary terms.
- Long-Term Impact: The full impact of AI may not be realized immediately. It often takes time for AI models to learn, adapt, and generate significant results.
- Data Dependency: AI’s performance is heavily dependent on the quality and availability of data. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to poor results and a lower ROI.
- Complexity: AI projects often involve complex algorithms, infrastructure, and integration with existing systems, making it difficult to isolate the specific contribution of AI to overall business outcomes.
- Evolving Technology: The rapid pace of AI innovation means that the technology landscape is constantly changing, making it challenging to establish consistent metrics and benchmarks.
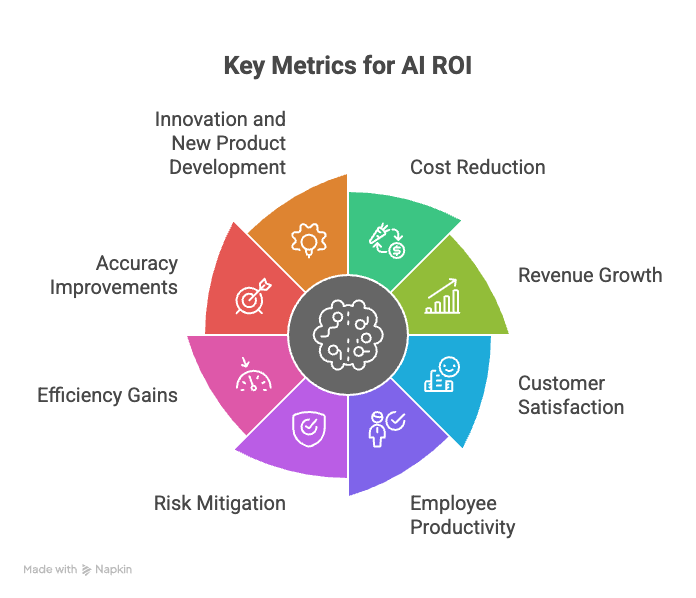
Key Metrics for Measuring AI ROI
Despite these challenges, it is essential to establish clear metrics for measuring the ROI of AI projects. These metrics should align with the organization’s strategic goals and provide a comprehensive view of AI’s impact. Here are some key metrics to consider:
- Cost Reduction: This metric measures the extent to which AI has reduced operational costs, such as labor, materials, or energy consumption. Examples include automating tasks, optimizing processes, and preventing errors.
- Revenue Growth: This metric tracks the increase in revenue generated as a result of AI initiatives. Examples include personalized recommendations, targeted marketing campaigns, and improved sales forecasting.
- Customer Satisfaction: This metric measures the impact of AI on customer satisfaction levels. Examples include AI-powered chatbots, personalized customer service, and proactive problem resolution.
- Employee Productivity: This metric assesses the extent to which AI has improved employee productivity. Examples include automating repetitive tasks, providing intelligent assistance, and streamlining workflows.
- Risk Mitigation: This metric measures the extent to which AI has reduced risks, such as fraud, security breaches, or compliance violations. Examples include AI-powered fraud detection systems, cybersecurity threat intelligence, and regulatory compliance monitoring.
- Efficiency Gains: This metric measures the improvements in efficiency achieved through AI implementation. This can be measured in terms of time saved, resources optimized, or output increased.
- Accuracy Improvements: In many AI applications, accuracy is a critical factor. Measuring improvements in accuracy, such as in predictive models or image recognition systems, can directly translate to ROI.
- Innovation and New Product Development: AI can drive innovation and enable the development of new products and services. Measuring the success of these new offerings can be a key indicator of AI’s ROI.
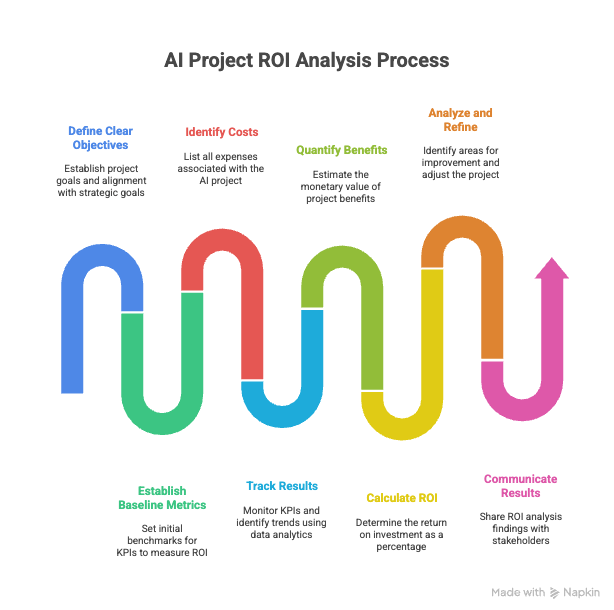
Framework for Measuring AI ROI
To effectively measure AI ROI, organizations should adopt a structured framework that encompasses the following steps:
- Define Clear Objectives: Clearly define the objectives of the AI project and how it aligns with the organization’s strategic goals. What specific business problems is the AI project intended to solve? What are the desired outcomes?
- Establish Baseline Metrics: Before implementing the AI project, establish baseline metrics for the key performance indicators (KPIs) that will be used to measure ROI. This will provide a benchmark against which to compare the results of the AI project.
- Identify Costs: Identify all the costs associated with the AI project, including development costs, infrastructure costs, data acquisition costs, and ongoing maintenance costs.
- Track Results: Continuously track the results of the AI project and compare them to the baseline metrics. Use data analytics tools to monitor KPIs and identify trends.
- Quantify Benefits: Quantify the benefits of the AI project in monetary terms whenever possible. This may involve estimating the value of intangible benefits, such as improved customer satisfaction or increased employee productivity.
- Calculate ROI: Calculate the ROI of the AI project by dividing the net benefits (benefits minus costs) by the total costs. Express the ROI as a percentage.
- Analyze and Refine: Analyze the results of the ROI calculation and identify areas for improvement. Refine the AI project based on the insights gained from the analysis.
- Communicate Results: Communicate the results of the ROI analysis to stakeholders, including senior management, project sponsors, and team members. This will help to build support for future AI initiatives.
Best Practices for Measuring AI ROI
In addition to the framework outlined above, here are some best practices for measuring AI ROI:
- Start Small: Begin with small, well-defined AI projects that have a clear business case and measurable outcomes. This will allow you to learn from your experiences and refine your approach before tackling larger, more complex projects.
- Focus on Business Outcomes: Focus on measuring the impact of AI on business outcomes, rather than simply measuring technical metrics. This will help to ensure that the AI project is aligned with the organization’s strategic goals.
- Use a Variety of Metrics: Use a variety of metrics to measure the ROI of AI projects, including both quantitative and qualitative metrics. This will provide a more comprehensive view of AI’s impact.
- Involve Stakeholders: Involve stakeholders from across the organization in the ROI measurement process. This will help to ensure that the metrics are relevant and that the results are credible.
- Be Transparent: Be transparent about the assumptions and limitations of the ROI analysis. This will help to build trust and credibility with stakeholders.
- Iterate and Improve: Continuously iterate and improve the ROI measurement process based on your experiences. This will help you to refine your approach and ensure that you are accurately measuring the value of AI.
Conclusion
Measuring the ROI of AI projects is essential for ensuring that AI investments deliver tangible business benefits. By adopting a structured framework, establishing clear metrics, and following best practices, organizations can effectively track and demonstrate the value generated by AI initiatives. This will enable them to make informed decisions about AI adoption, optimize their AI strategies, and drive sustainable growth. The key is to remember that AI ROI measurement is not a one-time event, but an ongoing process of monitoring, analysis, and refinement.
