Background
This blog explores the current state of AI and Computer Vision, highlighting recent advancements and future trends. It delves into the integration of these technologies across various industries, examining their impact and potential for further innovation. The document also addresses challenges and ethical considerations associated with the widespread adoption of AI and Computer Vision.
Current State of AI and Computer Vision
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Computer Vision (CV) have rapidly evolved from theoretical concepts to practical applications across numerous sectors. AI, encompassing machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL), provides the intelligence, while CV enables machines to “see” and interpret images and videos.
Key advancements include:
- Deep Learning: DL, particularly Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), has revolutionized image recognition, object detection, and image segmentation.
- Transfer Learning: Pre-trained models on large datasets can be fine-tuned for specific tasks, reducing training time and data requirements.
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): GANs are used for image generation, style transfer, and data augmentation.
- Edge Computing: Processing CV tasks on edge devices (e.g., smartphones, cameras) reduces latency and improves privacy.
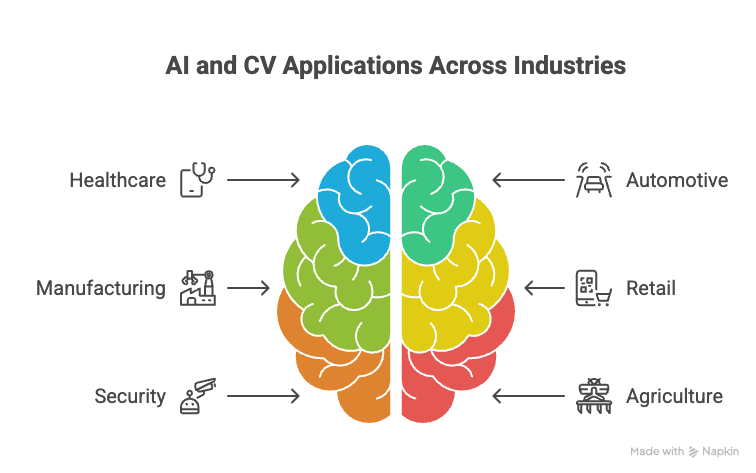
Applications Across Industries
The integration of AI and CV is transforming various industries:
- Healthcare: AI-powered image analysis aids in disease diagnosis, treatment planning, and drug discovery. CV is used in robotic surgery and patient monitoring.
- Automotive: Self-driving cars rely heavily on CV for object detection, lane keeping, and traffic sign recognition. AI algorithms handle decision-making and path planning.
- Manufacturing: CV enables quality control, defect detection, and predictive maintenance. AI optimizes production processes and improves efficiency.
- Retail: CV enhances customer experience through personalized recommendations, automated checkout systems, and inventory management.
- Security: AI-powered surveillance systems detect anomalies, identify threats, and improve security measures.
- Agriculture: CV monitors crop health, detects pests, and optimizes irrigation. AI analyzes data to improve yields and reduce resource consumption.
Future Trends
Several trends are shaping the future of AI and CV:
- Explainable AI (XAI): Making AI models more transparent and understandable to build trust and accountability.
- AI Ethics: Addressing ethical concerns related to bias, privacy, and security.
- Federated Learning: Training AI models on decentralized data sources while preserving privacy.
- Self-Supervised Learning: Training AI models on unlabeled data, reducing the need for expensive labeled datasets.
- AI-powered Video Analytics: Analyzing video streams in real-time for various applications, such as traffic management, crowd monitoring, and security.
- 3D Computer Vision: Reconstructing 3D models from images and videos for applications in robotics, augmented reality, and virtual reality.
- Neuromorphic Computing: Developing AI hardware inspired by the human brain, offering improved energy efficiency and performance.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the immense potential, AI and CV face several challenges:
- Data Requirements: Training deep learning models requires large amounts of labeled data, which can be expensive and time-consuming to acquire.
- Bias: AI models can inherit biases from the data they are trained on, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
- Security Vulnerabilities: AI systems are vulnerable to adversarial attacks, where malicious actors can manipulate inputs to cause errors or malfunctions.
- Computational Resources: Training and deploying complex AI models require significant computational resources, including GPUs and specialized hardware.
- Ethical Concerns: The use of AI raises ethical concerns related to privacy, security, and job displacement.
- Lack of Interpretability: Deep learning models are often “black boxes,” making it difficult to understand how they arrive at their decisions.
- Regulatory Landscape: The regulatory landscape for AI is still evolving, creating uncertainty for businesses and developers.
Overcoming the Challenges
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach:
- Data Augmentation: Techniques to artificially increase the size of training datasets.
- Bias Mitigation: Developing algorithms and techniques to detect and mitigate bias in AI models.
- Adversarial Training: Training AI models to be robust against adversarial attacks.
- Edge Computing: Deploying AI models on edge devices to reduce latency and improve privacy.
- XAI Techniques: Developing methods to make AI models more transparent and understandable.
- Ethical Guidelines: Establishing ethical guidelines and regulations for the development and deployment of AI.
- Collaboration: Fostering collaboration between researchers, developers, policymakers, and the public to address the challenges and opportunities of AI.
Conclusion
AI and Computer Vision are rapidly advancing, transforming industries and creating new opportunities. While challenges remain, ongoing research and development are paving the way for more robust, reliable, and ethical AI systems. The next level of AI and CV will be characterized by explainability, ethical considerations, and seamless integration into various aspects of our lives. By addressing the challenges and embracing the opportunities, we can harness the full potential of AI and CV to create a better future.