Background
Synthetic data generation is rapidly gaining traction as a powerful tool across various industries. This blog explores the potential benefits and risks associated with synthetic data, examining its applications, challenges, and ethical considerations. By understanding both the advantages and disadvantages, we can better leverage synthetic data to drive innovation while mitigating potential harms.
Introduction
Synthetic data or artificially created data that mimics the statistical properties of real-world data, is emerging as a transformative technology. It offers solutions to challenges related to data privacy, availability, and cost. However, the use of synthetic data also introduces new risks and considerations that must be carefully addressed.
Benefits of Synthetic Data
Enhanced Privacy
One of the most significant advantages of synthetic data is its ability to protect privacy. By training models on synthetic data instead of real data, organizations can avoid exposing sensitive information. This is particularly valuable in industries such as healthcare and finance, where data privacy regulations are stringent.
- Differential Privacy: Techniques like differential privacy can be applied during the synthetic data generation process to provide mathematical guarantees about the level of privacy protection.
- Reduced Risk of Re-identification: Synthetic data, when properly generated, does not contain any personally identifiable information (PII), reducing the risk of re-identification attacks.
Increased Data Availability
Synthetic data can overcome limitations in data availability. In situations where real data is scarce, expensive to collect, or subject to regulatory restrictions, synthetic data provides a viable alternative.
- Addressing Data Imbalance: Synthetic data can be used to augment datasets with under-represented classes, improving the performance of machine learning models.
- Enabling Research and Development: Researchers can use synthetic data to explore new ideas and develop innovative solutions without being constrained by data access limitations.
Cost Reduction
Generating synthetic data can be more cost-effective than collecting and processing real data. The cost savings can be substantial, especially in industries that require large datasets for training machine learning models.
- Reduced Data Acquisition Costs: Synthetic data eliminates the need to purchase or license real data, which can be expensive.
- Lower Data Storage and Processing Costs: Synthetic data can be generated on demand, reducing the need for large data storage infrastructure.
Accelerated Development
Synthetic data can accelerate the development of machine learning models by providing a readily available and customizable dataset.
- Faster Model Training: Synthetic data can be generated quickly and easily, allowing developers to train models more rapidly.
- Improved Model Performance: Synthetic data can be tailored to specific use cases, improving the accuracy and robustness of machine learning models.
Risks and Challenges of Synthetic Data
Fidelity and Accuracy
The effectiveness of synthetic data depends on its ability to accurately represent the statistical properties of real data. If the synthetic data is not sufficiently realistic, it can lead to biased or inaccurate models.
- Data Drift: Synthetic data may not capture changes in the real-world data distribution over time, leading to data drift and model degradation.
- Bias Amplification: If the real data contains biases, the synthetic data may amplify these biases, resulting in unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
Generation Complexity
Generating high-quality synthetic data can be a complex and computationally intensive process. It requires expertise in data modeling, machine learning, and statistical analysis.
- Model Selection: Choosing the right generative model for a specific dataset can be challenging.
- Parameter Tuning: Optimizing the parameters of the generative model to produce realistic synthetic data requires careful tuning and validation.
Evaluation and Validation
Evaluating the quality and utility of synthetic data is crucial to ensure that it is fit for purpose. However, this can be challenging, as traditional evaluation metrics may not be applicable.
- Utility Metrics: Developing appropriate metrics to measure the utility of synthetic data for specific tasks is an ongoing area of research.
- Real-World Validation: Validating the performance of models trained on synthetic data in real-world scenarios is essential to ensure that they generalize well.
Ethical Considerations
The use of synthetic data raises several ethical considerations, particularly in relation to privacy, fairness, and transparency.
- Privacy Paradox: While synthetic data is designed to protect privacy, it is important to ensure that it cannot be used to re-identify individuals or infer sensitive information.
- Bias and Fairness: Synthetic data can perpetuate or amplify biases present in the real data, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
- Transparency and Accountability: It is important to be transparent about the use of synthetic data and to establish clear lines of accountability for its impact.
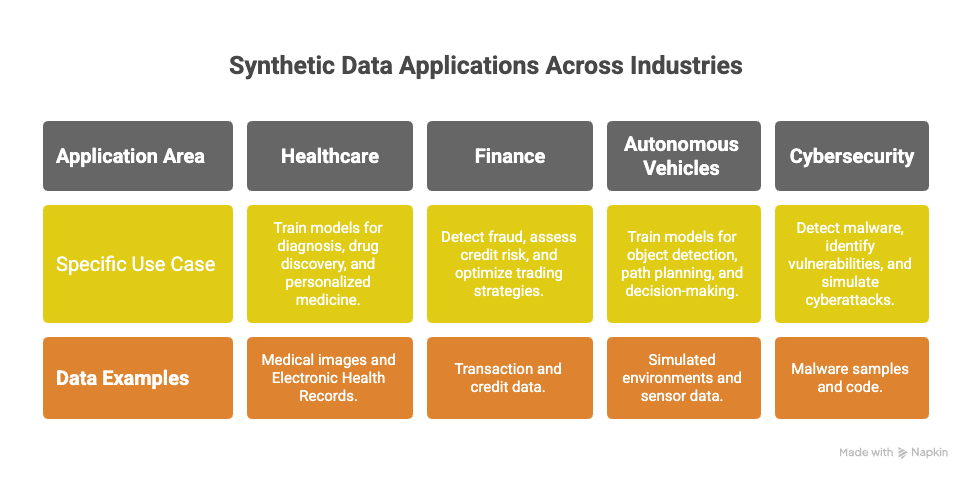
Applications of Synthetic Data
Healthcare
Synthetic data can be used in healthcare to train models for disease diagnosis, drug discovery, and personalized medicine.
- Medical Imaging: Synthetic medical images can be used to train models for detecting tumors, fractures, and other abnormalities.
- Electronic Health Records: Synthetic EHR data can be used to develop predictive models for patient outcomes and resource allocation.
Finance
Synthetic data can be used in finance to detect fraud, assess credit risk, and optimize trading strategies.
- Fraud Detection: Synthetic transaction data can be used to train models for identifying fraudulent activities.
- Credit Risk Assessment: Synthetic credit data can be used to develop models for predicting loan defaults.
Autonomous Vehicles
Synthetic data can be used in the development of autonomous vehicles to train models for object detection, path planning, and decision-making.
- Simulated Environments: Synthetic environments can be used to simulate a wide range of driving scenarios, including rare and dangerous situations.
- Sensor Data Generation: Synthetic sensor data, such as LiDAR and radar data, can be used to train models for perception and localization.
Cybersecurity
Synthetic data can be used in cybersecurity to detect malware, identify vulnerabilities, and simulate cyberattacks.
- Malware Detection: Synthetic malware samples can be used to train models for identifying malicious software.
- Vulnerability Assessment: Synthetic code can be used to identify potential vulnerabilities in software systems.
Conclusion
Synthetic data generation offers significant benefits in terms of privacy, data availability, cost reduction, and accelerated development. However, it also presents risks and challenges related to fidelity, complexity, evaluation, and ethics. By carefully considering these factors and implementing appropriate safeguards, organizations can harness the power of synthetic data to drive innovation while mitigating potential harms. As the technology continues to evolve, it is essential to stay informed about the latest advancements and best practices in synthetic data generation.
