Background
This blog explores the concept of Edge AI, focusing on its application in real-time processing scenarios. It delves into the advantages of deploying AI models at the edge, the challenges involved, and the various use cases where Edge AI offers significant benefits. The blog also discusses the hardware and software considerations for implementing Edge AI solutions, highlighting the importance of efficient model optimization and resource management.
Introduction to Edge AI
Edge AI refers to the deployment and execution of artificial intelligence (AI) models directly on edge devices, such as smartphones, embedded systems, IoT devices, and edge servers, rather than relying on centralized cloud servers. This approach brings AI processing closer to the data source, enabling real-time decision-making, reduced latency, enhanced privacy, and improved bandwidth utilization.
Advantages of Edge AI
- Reduced Latency: By processing data locally, Edge AI eliminates the need to transmit data to the cloud and back, significantly reducing latency. This is crucial for applications that require immediate responses, such as autonomous vehicles, robotics, and industrial automation.
- Enhanced Privacy: Processing data on the edge ensures that sensitive information remains on the device, reducing the risk of data breaches and privacy violations. This is particularly important for applications involving personal data, such as healthcare and surveillance.
- Improved Bandwidth Utilization: Edge AI reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted over the network, freeing up bandwidth and reducing network congestion. This is beneficial in scenarios where network connectivity is limited or unreliable.
- Increased Reliability: Edge AI enables applications to continue functioning even when the network connection is lost. This is critical for applications that require continuous operation, such as industrial control systems and emergency response systems.
- Lower Power Consumption: By processing data locally, Edge AI can reduce the power consumption of devices, extending battery life and reducing energy costs. This is important for battery-powered devices, such as IoT sensors and mobile devices.
Challenges of Implementing Edge AI
- Resource Constraints: Edge devices typically have limited processing power, memory, and storage capacity compared to cloud servers. This requires careful optimization of AI models to ensure that they can run efficiently on these devices.
- Model Optimization: Optimizing AI models for edge deployment involves techniques such as model compression, quantization, and pruning. These techniques reduce the size and complexity of the models without significantly sacrificing accuracy.
- Hardware Acceleration: Utilizing specialized hardware accelerators, such as GPUs, FPGAs, and ASICs, can significantly improve the performance of AI models on edge devices. However, these accelerators can add to the cost and complexity of the system.
- Security: Edge devices are often deployed in insecure environments, making them vulnerable to attacks. Security measures, such as encryption, authentication, and access control, are essential to protect the devices and the data they process.
- Software Frameworks: Selecting the appropriate software framework for Edge AI development is crucial. Frameworks like TensorFlow Lite, PyTorch Mobile, and ONNX Runtime provide tools and libraries for optimizing and deploying AI models on edge devices.
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: Implementing a robust OTA update mechanism is essential for keeping Edge AI models and software up-to-date with the latest security patches and performance improvements.
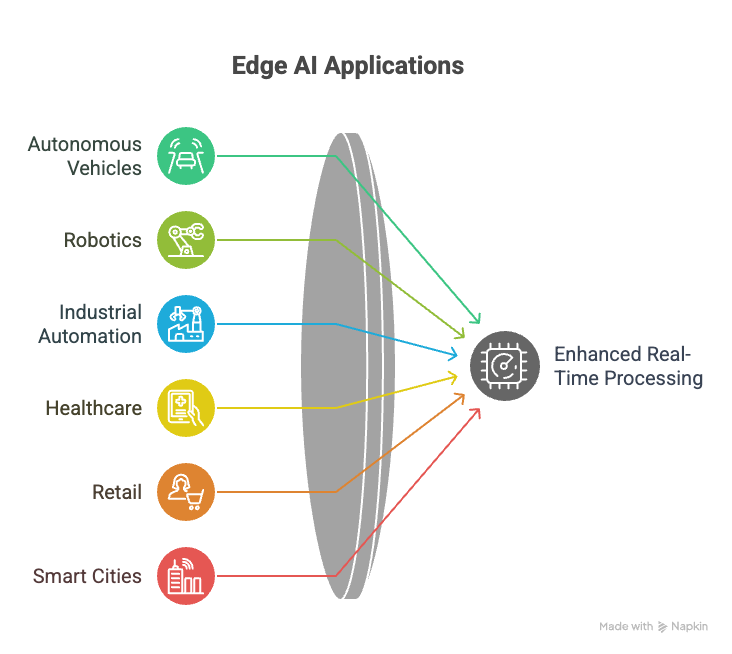
Use Cases of Edge AI
- Autonomous Vehicles: Edge AI enables autonomous vehicles to process sensor data in real-time, making decisions about navigation, obstacle avoidance, and lane keeping.
- Robotics: Edge AI allows robots to perform tasks such as object recognition, path planning, and manipulation in real-time, without relying on cloud connectivity.
- Industrial Automation: Edge AI enables real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes, improving efficiency, reducing downtime, and enhancing safety.
- Healthcare: Edge AI can be used for real-time patient monitoring, diagnosis, and treatment, improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
- Retail: Edge AI enables real-time analysis of customer behavior, optimizing store layouts, personalizing recommendations, and preventing theft.
- Smart Cities: Edge AI can be used for real-time traffic management, public safety monitoring, and environmental monitoring, improving the quality of life for citizens.
- Surveillance Systems: Edge AI enables real-time object detection, facial recognition, and anomaly detection in surveillance systems, enhancing security and reducing the workload on human operators.
- Agriculture: Edge AI can be used for real-time crop monitoring, disease detection, and irrigation control, improving crop yields and reducing resource consumption.
Hardware and Software Considerations
- Hardware Platforms: Selecting the appropriate hardware platform for Edge AI depends on the specific application requirements. Options include CPUs, GPUs, FPGAs, ASICs, and specialized AI accelerators.
- Operating Systems: Common operating systems for Edge AI include Linux, Android, and real-time operating systems (RTOS). The choice of operating system depends on the performance, security, and real-time requirements of the application.
- Software Frameworks: Software frameworks such as TensorFlow Lite, PyTorch Mobile, and ONNX Runtime provide tools and libraries for optimizing and deploying AI models on edge devices.
- Model Optimization Techniques: Model optimization techniques such as quantization, pruning, and knowledge distillation are essential for reducing the size and complexity of AI models without significantly sacrificing accuracy.
- Security Measures: Security measures such as encryption, authentication, and access control are crucial for protecting edge devices and the data they process.
Conclusion
Edge AI offers significant advantages for real-time processing applications, enabling reduced latency, enhanced privacy, improved bandwidth utilization, and increased reliability. While there are challenges associated with implementing Edge AI, such as resource constraints and security concerns, these can be addressed through careful model optimization, hardware acceleration, and robust security measures. As the demand for real-time AI applications continues to grow, Edge AI is poised to play an increasingly important role in various industries and domains. The key to successful Edge AI deployment lies in a holistic approach that considers both hardware and software aspects, along with a deep understanding of the specific application requirements.