Background
This blog explores the synergistic relationship between fine-tuning Large Language Models (LLMs) and leveraging Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) in conjunction with knowledge bases. We will delve into how these techniques can be combined to create more accurate, contextually relevant, and knowledgeable LLM applications. The blog will cover the benefits of each approach, the challenges involved, and practical strategies for effectively integrating them.
Introduction
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in various natural language processing tasks. However, they often suffer from limitations such as:
- Lack of up-to-date knowledge: LLMs are trained on vast datasets, but their knowledge is static and may not reflect the most recent information.
- Hallucinations: LLMs can generate factually incorrect or nonsensical information.
- Contextual limitations: LLMs may struggle to understand and respond appropriately to complex or nuanced queries.
To address these limitations, two prominent techniques have emerged: Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and fine-tuning.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
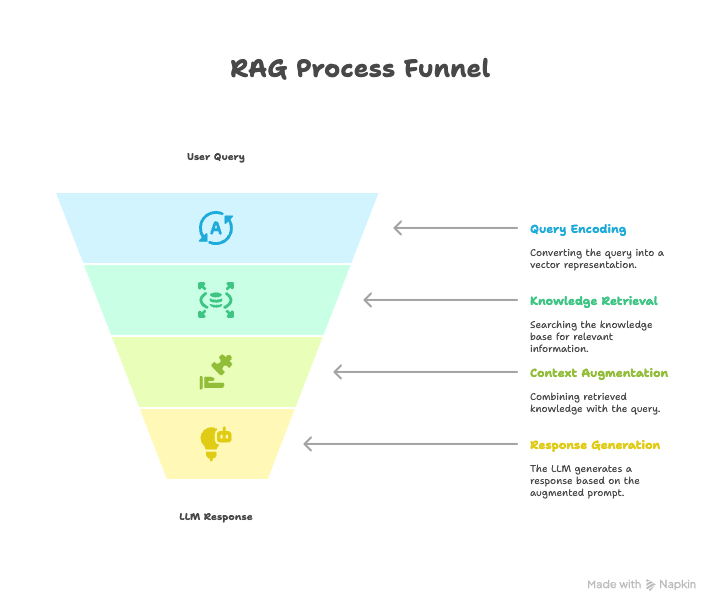
RAG enhances LLMs by providing them with external knowledge retrieved from a knowledge base. The process typically involves the following steps:
- Query Encoding: The user’s query is encoded into a vector representation.
- Knowledge Retrieval: The encoded query is used to search a knowledge base (e.g., a vector database, a document store) for relevant documents or passages.
- Context Augmentation: The retrieved knowledge is combined with the original query to create an augmented prompt.
- Generation: The augmented prompt is fed into the LLM, which generates a response based on both the query and the retrieved knowledge.
Benefits of RAG:
- Access to up-to-date information: RAG allows LLMs to access and incorporate the latest information from external sources.
- Reduced hallucinations: By grounding the LLM’s responses in retrieved knowledge, RAG can mitigate the risk of generating false or misleading information.
- Improved contextual understanding: RAG provides the LLM with additional context, enabling it to better understand and respond to complex queries.
Challenges of RAG:
- Retrieval accuracy: The effectiveness of RAG depends on the accuracy of the retrieval process. If irrelevant or incomplete knowledge is retrieved, the LLM’s response may be suboptimal.
- Knowledge base maintenance: Maintaining a comprehensive and up-to-date knowledge base can be a significant undertaking.
- Computational cost: Retrieving and processing knowledge can add to the computational cost of generating responses.
Fine-Tuning LLMs
Fine-tuning involves training an existing LLM on a smaller, task-specific dataset. This allows the LLM to adapt its parameters and improve its performance on the target task.
Benefits of Fine-Tuning:
- Improved task-specific performance: Fine-tuning can significantly improve the LLM’s accuracy, fluency, and relevance on the target task.
- Reduced reliance on prompt engineering: Fine-tuned LLMs may require less complex prompt engineering to achieve desired results.
- Customization: Fine-tuning allows for customization of the LLM’s behavior and style.
Challenges of Fine-Tuning:
- Data requirements: Fine-tuning requires a high-quality, task-specific dataset.
- Computational cost: Fine-tuning can be computationally expensive, especially for large LLMs.
- Overfitting: Fine-tuning can lead to overfitting, where the LLM performs well on the training data but poorly on unseen data.
- Catastrophic forgetting: Fine-tuning can cause the LLM to forget previously learned knowledge.
Combining RAG and Fine-Tuning
Combining RAG and fine-tuning can yield even better results than using either technique alone. There are several ways to integrate these approaches:
- Fine-tuning on RAG-augmented data: The LLM can be fine-tuned on a dataset that includes both the original queries and the retrieved knowledge. This allows the LLM to learn how to effectively utilize external knowledge.
- Fine-tuning the retrieval component: The retrieval component of the RAG pipeline can be fine-tuned to improve its accuracy and relevance. This can be done by training a separate model to rank or filter the retrieved documents.
- End-to-end fine-tuning: The entire RAG pipeline, including the LLM and the retrieval component, can be fine-tuned end-to-end. This allows for joint optimization of all components.
Benefits of Combining RAG and Fine-Tuning:
- Enhanced accuracy and relevance: By combining the strengths of both techniques, the LLM can generate more accurate and relevant responses.
- Improved generalization: Fine-tuning on RAG-augmented data can improve the LLM’s ability to generalize to new queries and knowledge sources.
- Reduced computational cost: Fine-tuning can reduce the need for extensive prompt engineering, which can save on computational costs.
Challenges of Combining RAG and Fine-Tuning:
- Increased complexity: Combining RAG and fine-tuning adds complexity to the development process.
- Data requirements: Fine-tuning on RAG-augmented data requires a large and diverse dataset.
- Optimization challenges: Optimizing the entire RAG pipeline can be challenging, as the different components may have conflicting objectives.
Practical Strategies
Here are some practical strategies for effectively integrating RAG and fine-tuning:
- Start with RAG: Begin by implementing a RAG pipeline and evaluating its performance. This will help you identify areas where fine-tuning can provide the most benefit.
- Curate a high-quality dataset: Invest time in curating a high-quality, task-specific dataset for fine-tuning. This dataset should include both the original queries and the retrieved knowledge.
- Experiment with different fine-tuning techniques: Explore different fine-tuning techniques, such as LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation), to find the best approach for your specific task.
- Monitor performance closely: Monitor the performance of the LLM after fine-tuning to ensure that it is not overfitting or forgetting previously learned knowledge.
- Iterate and refine: Continuously iterate and refine your RAG pipeline and fine-tuning process based on performance evaluations.
Conclusion
Combining RAG and fine-tuning offers a powerful approach to enhancing the capabilities of LLMs. By leveraging the strengths of both techniques, developers can create more accurate, contextually relevant, and knowledgeable LLM applications. While there are challenges involved in integrating these approaches, the potential benefits make it a worthwhile endeavor. By following the practical strategies outlined in this document, developers can effectively combine RAG and fine-tuning to unlock the full potential of LLMs.